Electrical Safety Compliance and Safety for Commercial Buildings
Ensuring electrical safety in commercial buildings is paramount for protecting the lives of occupants, safeguarding property, and maintaining the continuity of business operations. Adherence to...
Nov 01, 2024
# of Minutes to Read
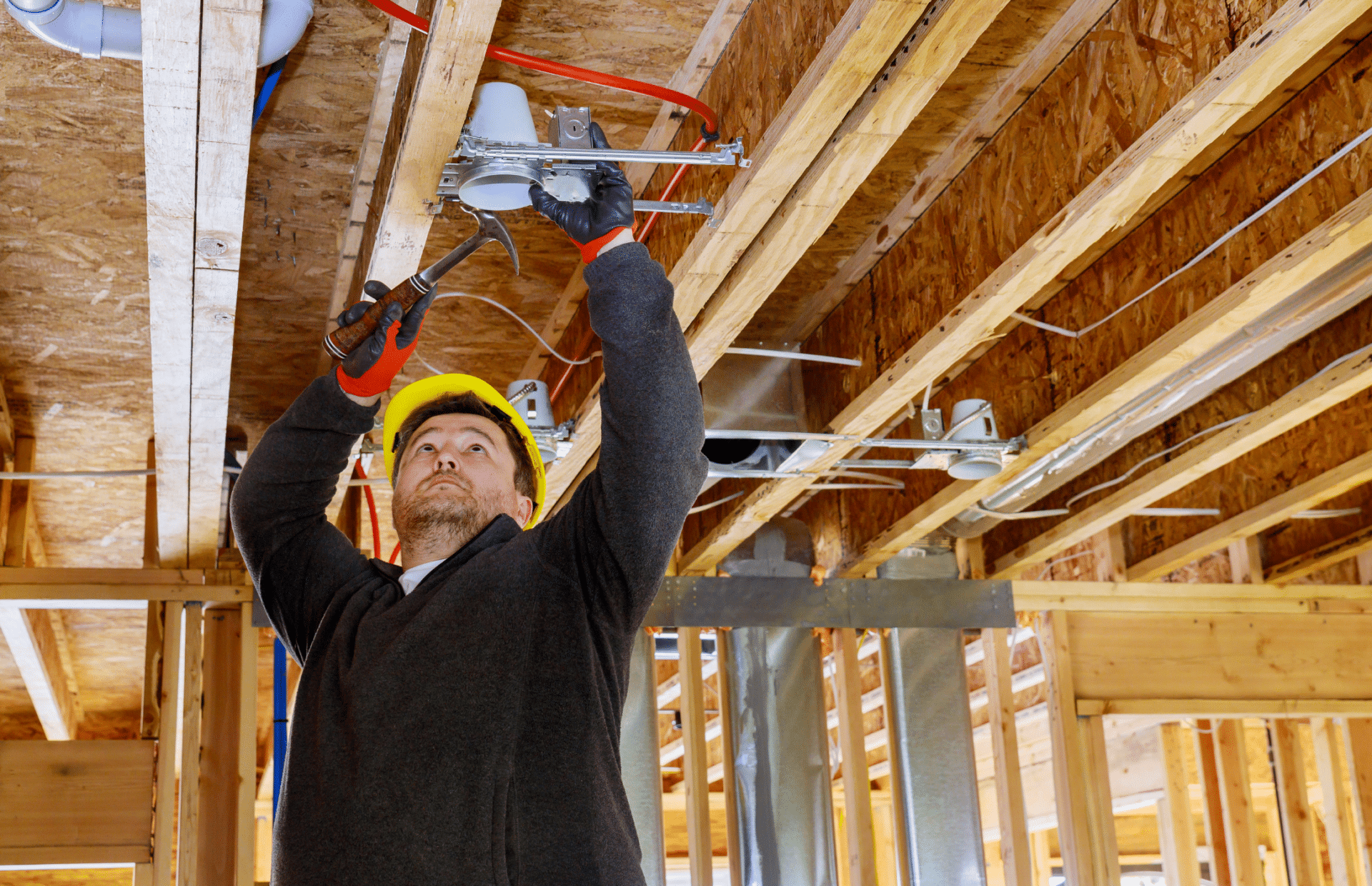

Ensuring electrical safety in commercial buildings is paramount for protecting the lives of occupants, safeguarding property, and maintaining the continuity of business operations. Adherence to electrical safety standards and compliance regulations is not only a legal requirement but also a critical aspect of facility management that can prevent costly accidents and downtime. This blog delves into the essential electrical safety standards and compliance measures that commercial buildings must follow to create a safe and efficient working environment.
Understanding Electrical Safety Standards
Electrical safety standards are guidelines and regulations designed to minimize the risk of electrical hazards such as shocks, fires, and explosions. These standards are developed by various organizations, including the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The primary standard governing electrical safety in commercial buildings is the National Electrical Code (NEC), also known as NFPA 70.
The National Electrical Code (NEC)
The NEC provides comprehensive guidelines on the installation, maintenance, and inspection of electrical systems in commercial buildings. It covers various aspects, including wiring methods, grounding, circuit protection, and the use of electrical equipment. Key provisions of the NEC include:
- Wiring and Protection: The NEC specifies the types of wiring materials and methods that are safe for different environments. It also outlines the requirements for circuit protection devices, such as circuit breakers and fuses, to prevent overloading and short circuits.
- Grounding and Bonding: Proper grounding and bonding are essential for preventing electrical shocks and fires. The NEC mandates the use of grounding conductors and bonding connections to ensure that electrical systems are safely grounded.
- Equipment Installation: The NEC provides guidelines for the installation of electrical equipment, including lighting fixtures, switches, and outlets. It ensures that these installations meet safety requirements and are suitable for their intended use.
- Safety-Related Work Practices: The NEC emphasizes the importance of safe work practices, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), lockout/tagout procedures, and regular safety training for employees.
OSHA Regulations
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets forth regulations to protect workers from electrical hazards in the workplace. OSHA’s electrical safety standards, found in 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S, are designed to complement the NEC by focusing on safe work practices and procedures. Key OSHA requirements include:
- Electrical Safety Programs: Employers must develop and implement an electrical safety program that includes regular inspections, maintenance, and testing of electrical systems. The program should also include procedures for responding to electrical emergencies.
- Employee Training: Workers who are exposed to electrical hazards must receive adequate training on safe work practices, hazard recognition, and the proper use of PPE. This training should be documented and regularly updated.
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: OSHA requires the use of lockout/tagout procedures to ensure that electrical systems are de-energized and cannot be accidentally re-energized during maintenance or repair work.
- Hazard Communication: Employers must inform workers about the electrical hazards present in their workplace and provide clear labeling and signage to identify hazardous areas and equipment.
IEEE Standards
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) develops standards that provide additional guidance on electrical safety and reliability. IEEE standards, such as IEEE 1584 for arc flash hazard analysis and IEEE 3000 series for power system design, offer detailed methodologies and best practices for assessing and mitigating electrical risks. Key IEEE contributions include:
- Arc Flash Hazard Analysis: IEEE 1584 provides a method for calculating the potential energy of an arc flash and determining the appropriate PPE and protective measures to reduce the risk of injury.
- Power System Design: The IEEE 3000 series covers various aspects of power system design, including system reliability, protection coordination, and energy efficiency. These standards help ensure that electrical systems are designed to meet safety and performance requirements.
Compliance and Inspections
Compliance with electrical safety standards involves regular inspections and audits to ensure that electrical systems are properly installed and maintained. Key steps for achieving compliance include:
- Periodic Inspections: Regular inspections by qualified personnel are essential for identifying potential hazards and ensuring that electrical systems comply with safety standards. Inspections should include visual checks, testing of electrical equipment, and verification of proper grounding and bonding.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of inspections, maintenance activities, and employee training is crucial for demonstrating compliance with electrical safety standards. These records should be readily available for review by regulatory authorities.
- Third-Party Audits: Engaging third-party auditors can provide an independent assessment of electrical safety compliance and identify areas for improvement. Auditors can also offer recommendations for enhancing safety programs and procedures.
Best Practices for Electrical Safety
In addition to adhering to regulatory requirements, electricians and facility managers can implement best practices to further enhance electrical safety. These best practices include:
- Preventive Maintenance: Implementing a preventive maintenance program for electrical systems can help identify and address potential issues before they become serious hazards. This includes regular testing and calibration of protective devices, cleaning and inspection of electrical panels, and replacing worn or damaged components.
- Risk Assessment: Conducting a thorough risk assessment of electrical systems can help identify potential hazards and prioritize mitigation measures. This includes evaluating the condition of electrical equipment, analyzing the potential for arc flash incidents, and assessing the overall reliability of the power system.
- Employee Engagement: Encouraging employees to actively participate in electrical safety programs can help create a culture of safety in the workplace. This includes involving workers in safety meetings, soliciting feedback on safety practices, and recognizing employees who demonstrate a commitment to safety.
- Clear Signage and Labeling: Ensuring that all electrical panels, circuits, and equipment are clearly labeled with appropriate signage. This helps workers quickly identify electrical hazards and take necessary precautions.
- Emergency Response Plan: Developing and regularly updating an emergency response plan for electrical incidents. This plan should include procedures for reporting electrical hazards, responding to electrical emergencies, and providing first aid to injured workers.
- Proper Housekeeping: Maintaining a clean and organized work environment to reduce the risk of electrical accidents. This includes keeping electrical panels accessible, avoiding the use of extension cords as permanent wiring, and ensuring that electrical equipment is properly stored when not in use.
Electrical safety standards and compliance are critical for protecting the well-being of occupants, safeguarding property, and ensuring the smooth operation of commercial buildings. By adhering to regulations such as the NEC, OSHA standards, and IEEE guidelines, electricians and facility managers can create a safe and efficient electrical environment. Regular inspections, proper documentation, and the implementation of best practices further enhance electrical safety and help prevent costly accidents and downtime. By prioritizing electrical safety, commercial buildings can achieve regulatory compliance and foster a culture of safety that benefits everyone.
Implementing and maintaining electrical safety standards requires a proactive approach, continuous monitoring, and a commitment to safety from all stakeholders involved. For electricians and facility managers, understanding and adhering to these standards is not only a regulatory obligation but also a vital step in ensuring the longevity and reliability of their electrical systems.
Ready to streamline your electrical safety and compliance processes? RazorSync’s powerful field service management software can help you manage inspections, maintenance schedules, and compliance documentation with ease. Experience the benefits of comprehensive customer education and dedicated support to ensure your team leverages our tools to their full potential. Start your free trial today and see how RazorSync can transform your electrical service operations! Start Your Free Trial.